Using four images
Here is presented the scenario used in the EYE+ XTD hand-eye calibration wizard. In this scenario, EYE+ XTD should detect only one part per image and for each detected part, you should associate a robot position. Once this scenario is finished, you will get the coordinates of the part directly in the robot frame during production.
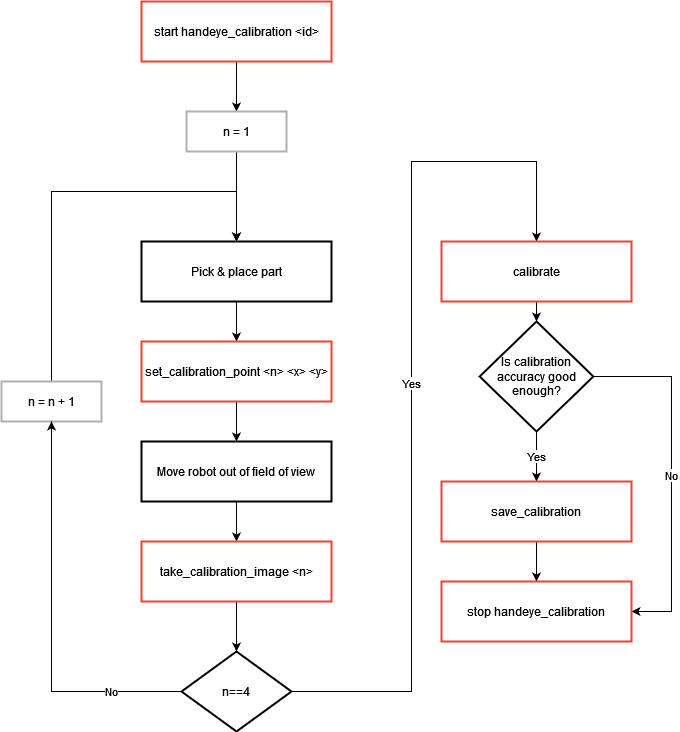
Fig. 202 Hand-eye calibration using four images
[start handeye_calibration <id>]: Start the hand-eye calibration state using the correct recipe identifier
<id>.
Start a loop of four iterations
[Pick & place part]: Pick a part and place it in the picking area. When picking the part, make sure you pick it from the pick point defined in the selected recipe. The part must be placed in such a way that it can be detected by EYE+ XTD in the next image analysis. A good practice is to place the part as close as possible to a corner of the picking area and at each iteration in a different corner.
[set_calibration_point <n> <x> <y>]: Once you have placed the part, collect the actual coordinates of the robot and send them to EYE+ XTD using the command set_calibration_point with the correct point number
<n>.[Move robot out of field of view]: Move the robot out of the field of view without moving the part.
[take_calibration_image <n>]: Call the take_calibration_image command with the same
<n>number used for the previous set_calibration_point command.
Once the loop is finished
[calibrate]: Call the calibrate command and check if the
calibration_accuracyis good enough for your production scenario. If it is not, you probably need to check the following things:Is the tool of your robot correctly defined?
Did you pick the part correctly?
Is your recipe precise enough?
Did the part move during the scenario?
Note
Frequent pick failures during production may indicate that your hand-eye calibration is not accurate enough. In such cases, performing a new calibration can help improve system performance.
However, note that a failed pick does not necessarily result from poor calibration. Other factors such as mechanical issues may also be involved.
For guidance on improving calibration accuracy, refer to How can I increase hand-eye calibration accuracy?.
Note
You can test the calibration using the command test_calibration.
[save_calibration]: Save the hand-eye calibration by using the command save_calibration.
[stop handeye_calibration]: To stop the hand-eye calibration state, call the command stop handeye_calibration.